Technology Insight Report - Graphene.pdf
Summary
This report covers patent analysis on the use and application of graphene, its research momentum and key intellectual property indicators. Owing to their specialized structures and minute diameter, it can be utilized as a sensor device, semiconductor, or for components of integrated circuits. Patent data reveals various organizations have focused their research across different categories and application areas of graphene. It provides scope for researches that can chance the path of quantum physics. This report focuses on how Patent data can help uncover the trends, gaps and opportunities that exist around this area. You will find the information on the research activity, application areas, the companies most active in this research area, the filings spread, key comparisons etc. This report was prepared by mining patent data using Patent iNSIGHT Pro, a comprehensive patent analysis platform that helps one accelerate time-to-decision from patent analysis activities.
Overview
Graphene with the unique combination of bonded carbon atom structures with its myriad and complex physical properties is poised to have a big impact on the future of material sciences, electronics and nanotechnology.Owing to their specialized structures and minute diameter, it can be utilized as a sensor device, semiconductor, or for components of integrated circuits. The reported properties and applications of this two-dimensional form of carbon structure have opened up new opportunities for the future devices and systems.
Introduction to Graphene
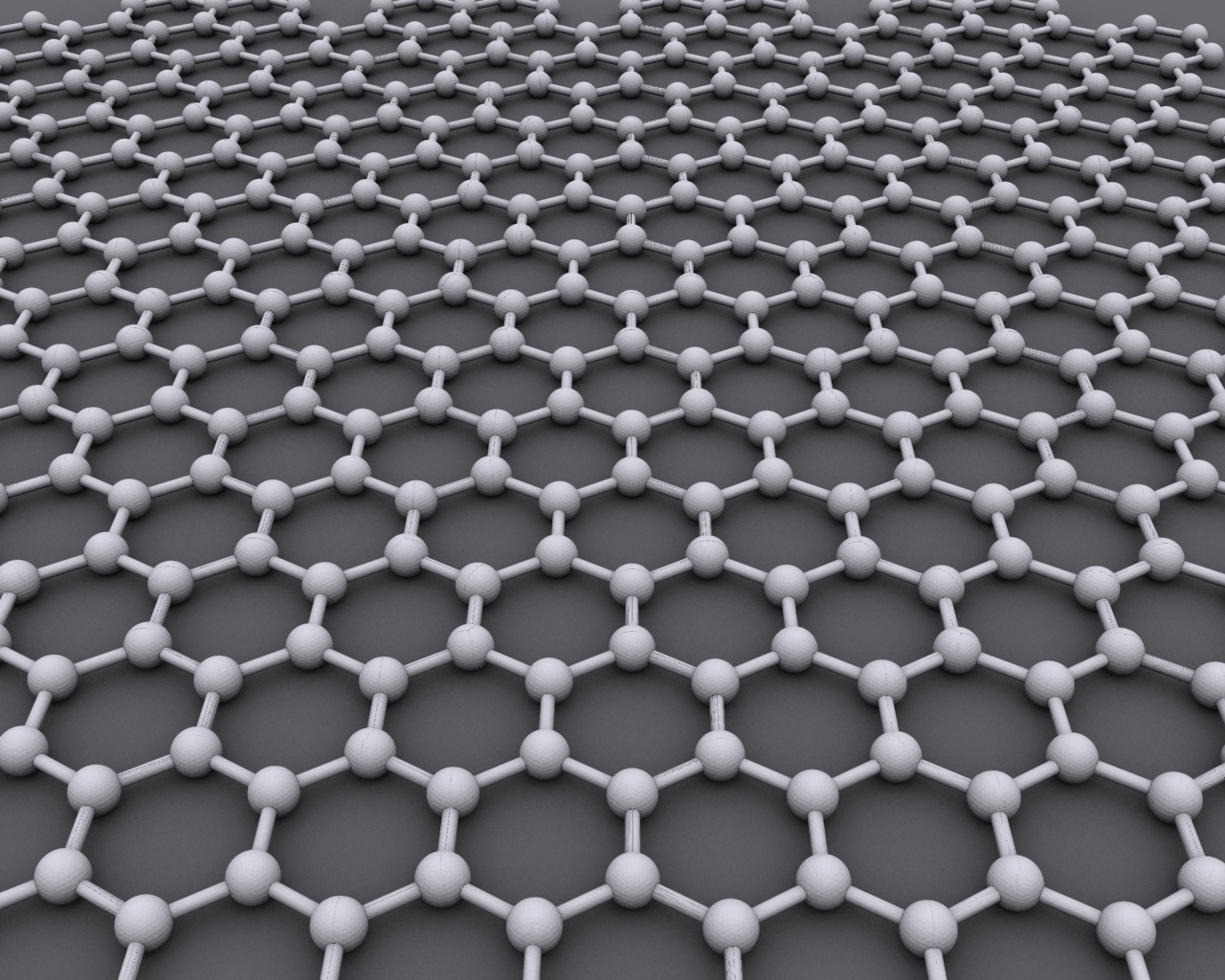
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer carbon foils in 1962. Graphene is most easily visualized as an atomic-scale chicken wire made of carbon atoms and their bonds. The crystalline or "flake" form of graphite consists of many graphene sheets stacked together.
The carbon-carbon bond length in graphene is about 0.142 nanometers.Graphene sheets stack to form graphite with an interplanar spacing of 0.335 nm, which means that a stack of 3 million sheets would be only one millimeter thick. Graphene is the basic structural element of some carbon allotropes including graphite, charcoal, carbon nanotubes and fullerenes. It can also be considered as an indefinitely large aromatic molecule, the limiting case of the family of flat polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The Nobel Prize in Physics for 2010 was awarded to Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov "for groundbreaking experiments regarding the two-dimensional material graphene". Click Here to read more.
Comments